Service Resolution¶
An OData service usually starts with "/" which delivers the service document while all preceding path segments belong to the servlet and servlet mapping of a web application.
Some service providers would like to get control over the path hierarchy. This is called service resolution. Actually it means an OData path can start at any hierarchy path level behind the service mapping path elements.
An uri schema with and without service resolution is shown here:
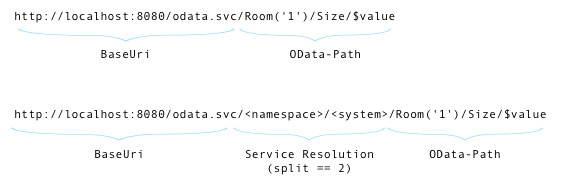
A service init parameter (org.apache.olingo.odata2.path.split) can be set for servlet configuration (see web.xml) and define how many path segments are not interpreted as OData path segments. In the example the split value is 2 and the resulting service resolution uses two path segments. The first one is for
<?xmlversion="1.0"encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-appxmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee"xmlns:web="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd"
id="WebApp_ID"version="2.5">
<display-name>MyApp</display-name>
<welcome-file-list>
<welcome-file>index.jsp</welcome-file>
</welcome-file-list>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>ODataServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.apache.cxf.jaxrs.servlet.CXFNonSpringJaxrsServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>javax.ws.rs.Application</param-name>
<param-value>org.apache.olingo.odata2.core.ODataApplication</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>org.apache.olingo.odata2.service.factory</param-name>
<param-value>org.apache.olingo.odata2.ref.processor.ScenarioServiceFactory</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>org.apache.olingo.odata2.path.split</param-name>
<param-value>2</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>ODataServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/odata.svc/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
A processor implementation (e.g. ODataSingleProcessor) does have access to an ODataContext object which will deliver a PathInfo object.
From this class a processor implementation can access the service resolution information which is as following:
- URI: http://localhost:8080/odata.svc/[namespace]/[system]/Room('1')/Size/$value
- preceding path segments: [namespace], [system]
- OData path segments: Room('1'), Size, $value
- base URI: http://localhost:8080/odata.svc/[namespace]/[system]/
Sample Code
public interface ODataContext {
ODataService getService() throws ODataException;
PathInfo getPathInfo() throws ODataException;
}
public interface PathInfo {
List<PathSegment> getPrecedingSegments();
List<PathSegment> getODataSegments();
URI getServiceRoot();
URI getRequestUri();
}
Copyright © 2013-2025, The Apache Software Foundation
Apache Olingo, Olingo, Apache, the Apache feather, and
the Apache Olingo project logo are trademarks of the Apache Software
Foundation.

